How to properly defrost food?
August 4, 2025
How Data Becomes the Power Behind Supply Chain Control
August 12, 2025The Importance of Calibration in Production and the Kitchen: Ensuring Accuracy and Safety.Ensuring accuracy and safety is essential when a business operator is engaged in the food production sector. Calibration is a critical process in both production and kitchen environments. It involves comparing the measurements of an instrument or equipment to approved standards to ensure accuracy and reliability. The goal of calibration is to identify any discrepancies and adjust the instrument accordingly to align with the standard. This process is vital for maintaining product integrity and quality, especially in food production and storage.
In today’s blog, the Food Safety Alliance will share all the key details that will help you improve your working environment.
What is Metrology?

Metrology is the science of measurement. It includes all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement, ensuring the accuracy and consistency of measurements. In the context of calibration, metrology provides the principles and techniques used to achieve precise measurements. Metrology is essential in various industries, including food production, where accurate measurements are crucial for safety, quality, and compliance.
The Role of Calibrated Equipment in Food Production and Storage
In food production and storage, calibrated equipment ensures that environments and processes meet strict safety and quality standards. Below are several key tools for which calibration plays a significant role:
Thermometers: Accurate temperature control is essential in food production to prevent spoilage and microbiological contamination. Calibrated thermometers ensure that preparation, storage, and processing temperatures remain within safe limits.
Manometers: These instruments measure pressure levels in various equipment, such as ovens and pressure cookers. Proper calibration ensures these devices operate within safe and effective pressure ranges, which is important for maintaining food quality and safety.
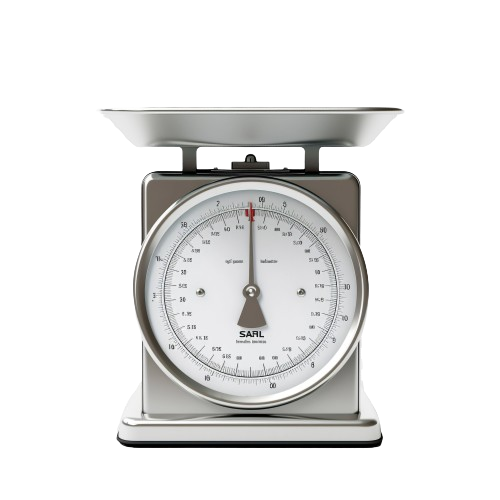
Scales: Accurate ingredient measurement is vital in food production. Calibrated scales ensure consistency in recipes and compliance with nutritional standards.
Humidity Sensors: In storage areas, humidity control is crucial to prevent mold growth and spoilage. Calibrated humidity sensors help maintain optimal storage conditions.
Calibration Frequency
![]()
The frequency of calibration depends on several factors, including the type of equipment, its usage, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. In general, the following guidelines are applied:
Thermometers and Manometers: Should be calibrated at least once a year. More frequent calibration may be required for high-usage or critical operations.
Scales: Monthly or quarterly calibration is recommended, especially in high-volume production environments.
Humidity Sensors: Calibration should be performed every six months to ensure accuracy.
Regular calibration schedules help maintain measurement reliability and prevent equipment defects over time, ensuring consistent quality and safety in food production.
Calibration and PRP/GMP Requirements

Prerequisite Programs (PRP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are fundamental elements in food safety management systems.
They provide the essential environmental and operational conditions required for the production of safe food. Calibration is a key component of these programs:
PRP Requirements:
PRPs outline general conditions needed in food production facilities, including equipment maintenance and calibration. Ensuring all measurement instruments are calibrated supports compliance with these requirements and helps prevent contamination or quality issues.
GMP Standards:
GMP requires that all equipment used in production processes be properly maintained and calibrated. This includes regular inspections and documentation to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards.
Calibration and HACCP:
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a systematic food safety approach that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards. Calibration is an integral part of the HACCP system for several reasons:
Identifying Critical Control Points (CCPs): Accurate measurements are essential for effectively identifying and monitoring CCPs. For example, maintaining a specific temperature to eliminate pathogens is a critical control point that relies on calibrated thermometers.
Monitoring CCPs: Ongoing CCP monitoring requires reliable instruments. Calibration ensures these tools provide accurate data, which is crucial for making informed food safety decisions.
Documentation and Verification:
HACCP demands thorough documentation and verification of all processes. Calibration records serve as evidence that equipment functions correctly and that the HACCP system is effective.
Conclusion

Calibration is a key link to quality and safety in both production and kitchen environments. By ensuring that instruments such as thermometers, manometers, scales, and humidity sensors provide accurate measurements, businesses can maintain high standards of food safety and quality. Regular calibration, aligned with metrology principles, supports compliance with PRP, GMP, and HACCP requirements, protecting end consumers and enhancing product reliability.
Implementing and maintaining a regular calibration program not only meets regulatory standards but also fosters trust and reliability in food production and storage. By prioritizing calibration, manufacturers and kitchen staff can ensure their operations are safe, efficient, and consistent.
For more information on how to organize your kitchen, you can read the blog below.